

Top Quality Iranian Saffron


Supply over 1000Kg monthly



Saffron is the most valuable plant species in the world, because each kilogram of this product is about 170,000 saffron flowers. This plant has been linked to the culture and history of Iranian people during a 2500 years and it has been one of the main sources of income for people and the native farmers of this dry and semi-dried land in all these centuries. The indigenous farmers of this region and the regions with similar climate in Iran, have been so smart, to produce the mass production of this product with the best quality and quantity, which is a plant with minimum water requirement and it is why Iran is the largest saffron producer in the world. Iranians, while have been exported saffron to different parts of the world, taught foreign people about saffron uses and properties, they also taught other people how to cultivate saffron.
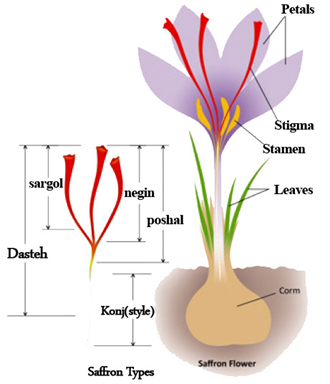
Saffron is a small, multi-annual plant with an approximate height of 10 to 20 centimetres, with narrow, long leaves that have been ejected from the middle of the corm. These leaves have a stem with flower which ends with one to three flowers. Each one of these flowers has six petals that are purple. Each flower has three stamens and an anther leading to a three-branched stigma in a bright red colour. This style and the red colour stigma at the end of the style are the famous, fragrant and flavoured part of saffron plant that is used.

In the harvest season of saffron, which usually begins in mid-November, depending on the onset of cold, saffron flowers should be collected from the farm every day and transferred to the manufactory for drying. The sooner saffron flowers are gathered, they have better quality and product. In many cases, it is done early in the morning and even before the sunrise. Because the sun decreases the amount of saffron dyeing also, it should be noted that saffron flowers should eventually be collected from the plant for up to 48 hours after growing, otherwise they will be lost and completely transformed into garbage. After harvesting the flowers and transferring them to the manufactory, the saffron stigma with style, as a whole and interconnected, is removed from the leaves, which is the same portion of saffron consumable in various uses and industries.

Different types of saffron are based on the cut location of stigma and its drying method:
1- Saffron in a bunch: When the entire saffron stigma, with its style, is removed from the plant completely and will be dried without cutting.
2- Negin saffron: When the full wet saffron filament is cut from the junction of the three-branched red stigma, separated from the white part, dried, this type of saffron which is completely prominent and scaly form is called Negin and it is almost the best, the most expensive and most valuable type of saffron. In the Persian literature, Negin is said to a very precious stone, high-quality, brilliant and highlighted which is placed on a gold ring. Negin has been named for this type of saffron because of its value and beauty and brilliance.
3- Sargol saffron: When the red part of the saffron stigma is broken down and removed from the saffron bunch, the red dried saffron filaments has lost its scaly and three-branched connection form due to the breakage of the stigma, and it’s seen in form of dried, relatively flat and broken filaments.
4- Pooshal saffron: When the wet three-branched red colour stigma with its orange end is been removed and dried. Pooshal Saffron which can easily been recognized by its orange end, has different grades according to its orange end size. The smaller the length and size of the orange part, the saffron will be more favourable due to its better colour number.
5- White saffron (Konj): After removing the red part from the wet Negin saffron, or the red and orange part in Pooshal saffron, the style and white part of saffron remains and these parts will be dried and used in special cases and uses. It should be noted that the white part of saffron has almost all the properties of saffron, such as aroma, flavour, etc., except the colour. Therefore, they use white part in a kind of industry, which only needs the aroma or taste of saffron and does not require red colour. For example, in the culinary industry, when it is needed to have the aroma and taste of saffron, without changing the colour, like cooking some types of fish, the white of saffron will be used.

Saffron can have varying degrees of quality depending on the climate and age of the agricultural land as well as different methods of planting and harvesting. Part of the quality difference in different types of saffron is visible apparently, such as coarseness, tiny, crop failure or the presence of different types of saffron waste. In order to understand more profoundly and to observe the differences more fundamental, and to identify the quality of the product more accurately, it is necessary to perform several tests on saffron in the laboratory.
These tests can be several physical or chemical tests, such as color strength testing, additives or impurities of saffron, bitterness, etc., or microbial tests such as bacteria assaying. The obtained product, in all its types, can range from grade 1 to grade 4, according to the scientific standards defined for various types of saffron. The saffron of all types, offered by Iran Commerce, are the grade 1 and it has been proved after all physical, chemical and microbial tests. No lower quality saffron can be added to Iran Commerce collection. The figure below depicts the exclusive laboratories of saffron provided by Iran Commerce.

For this purpose, we need a healthy and not crushed or powdered saffron filament. Pour some of the saffron filaments on a little glass of warm water.
First:
Genuine saffron is never settled down immediately and remains on the water. Of course, saffron filaments, like any other substance, become softer after dampening and be settled, but this may happen after a few hours, but they will never be immediately settled down. The rapid deposition of saffron filaments indicates that these filaments may be anything but saffron and basically the filaments under test are not saffron.
Second:
Saffron spilled in water should never seep red colour. The original saffron gently unlocks its colour in the water and initially gives the water a yellowish lustre, and by the time, this colour is enhanced and, depending on the quality of the sample, it makes the water yellow. After about a few hours, the water colour will become almost orange. If the saffron solution turns out to be red, it means that the tested filaments has an additive red colour, which is added to it, and releases this additive colour in water during the test.
Third:
Sometimes the fraudulent add an additive red colour to their white part of saffron (style) and sell this saffron instead of high quality saffron to the consumer. In this case, when the saffron filaments spilled on water they lose their additive colour; and then they go back to their original colour which is white. By looking at them, it is perfectly understandable that these are saffron white part, which are much cheaper than genuine saffron, which remained poured on the water like white filaments after releasing their additive colour.
Fraudulent always sell these products to consumers for their benefits and profits, without considering the consumers' health, and abuse the public's lack of proper knowledge. While, based on experience and research, the consumption of fake saffron is dangerous and in some cases cancerous. Therefore, it has always been necessary to inform saffron consumers accurately to take a small step, to protect the health and food safety of the community.
Tips on saffron storage:
Saffron should be kept in a cool, dry place away from sunlight. Heat and moisture can cause saffron to damage by pest or mildew, and light can also affect the colouring power of saffron by reducing its colour.

We have read in the history that people have always used saffron extract as a soothing medicine. They have reported that the only effective medication and painkiller for severe pain in the Timur leg Mogul ruler, was extract and combination obtained from saffron juice.
Nowadays, with the development of medical knowledge, and the expansion of the pharmaceutical industry, it has become clear that the ingredients in saffron have various medical properties. Properly consumed, as recommended by physicians, can be so beneficial, and over-consumption can impair the health.
Daily, a small amount of brewed saffron strands, with tea, can greatly relax one's thoughts and moods. The natural vitality of drinking saffron tea is one of the unique properties of this exceptional plant.

The unique and exclusive physical and chemical properties of saffron, with its high purity and quality, on the one hand, and the tendency of various industries to use natural, non-industrial and non-laboratory raw materials, on the other hand, have led to many industries to use saffron as an important but precious raw material. Industries such as:
• Cosmetics Manufacturing Industries
• Perfume and Cologne Industries
• Hygienic Manufacturing Industries
• Pharmaceutical Industries
• Dyeing Industries
• Alcohol and non-alcoholic beverage industries
And in many other industries, each one uses saffron to produce very high quality products.

In many countries, especially Asian countries, saffron is used as an important ingredient in the preparation of various home-made foods. The unique aroma, the beautiful color and the unique taste of saffron have a great impact on the cooking of delicious and lovely dishes. In many international hotels and restaurants, of course, saffron, as the most expensive spice in the world, plays an important role in the food menu of famous chefs in preparing expensive and luxurious dishes. The presence of saffron in different foods not only makes them more delicious, but also it has important effects on human health.
Copyright 2019 © IRAN Commerce Co.